Privacy Canada is community-supported. We may earn a commission when make a purchase through one of our links. Learn more.
How Torrenting Laws Work in Canada – What You Need to Know
Whenever someone mentions ‘torrent,’ there’s an immediate association with illegal downloads and internet piracy. Right? The word often conjures images of internet piracy, which is associated with a pretty hefty negative stigma. And frankly, it’s clear why: the method is notoriously linked to sharing copyrighted music, movies, and games.
But let’s clear the air. Not all uses of torrenting cross legal boundaries. So, let’s address a burning question: ‘Is torrenting illegal in Canada?’
Before you venture into downloading your next file from what is touted as the best torrent sites in Canada, here are some crucial points you should understand to avoid inadvertently stepping over legal lines.
Understanding the Basics: What is Torrenting?
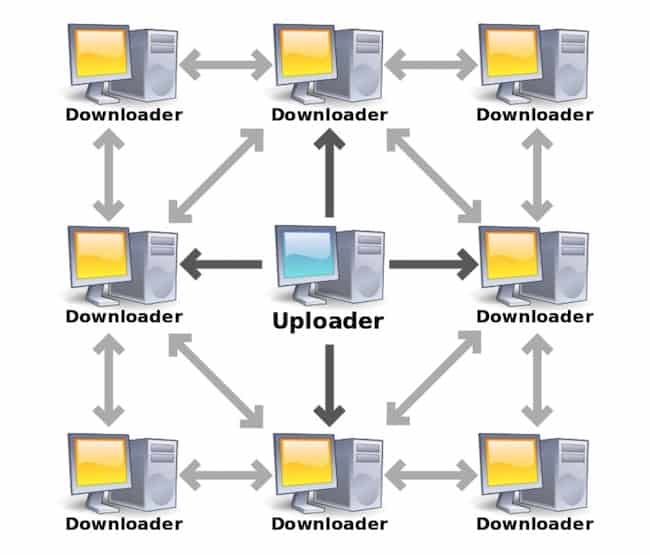
Think of torrenting as simply downloading and uploading files, but with a twist. You use something called the BitTorrent protocol, which connects you to a whole network of users—just regular folks, really. These users are known as ‘peers,’ and because they exchange files directly among themselves, without any middleman, this system is called ‘peer-to-peer’, or ‘P2P’ for short.
So, instead of downloading a file from a single central server, leeches (users who download files using torrenting) download pieces of the file from different peers. At the same time, seeders (users who upload and share those files) might be sharing pieces of the file with others. This sharing and receiving of files among peers is precisely what makes the network decentralized and efficient.
To start sharing files, you’ll need to hook up to the BitTorrent network.
But how?
First, grab a torrent client—popular ones include qBittorrent, uTorrent, Vuze, and Deluge. Once you’ve got that set up, you’ll use something called a .torrent file or a magnet link. These are like special keys that connect your torrent client directly to the torrent you’re after.
As a result, the files remain on the devices of the torrent swarm—leeches and seeders.
Is Torrenting Illegal?
Torrenting in itself is entirely legal. In fact, there isn’t any country where torrenting or visiting torrent sites is illegal on its own.
Rather, the legality of your activity depends on the content you’re torrenting since it can violate copyright laws, which naturally differ from country to country.
Therefore, while it has plenty of legal uses, its P2P method can also be used to share unsanctioned files. By that, we mean copyrighted movies, unauthorized software, pirated music or unlicensed games. That’s when torrenting becomes unlawful.
Copyright Laws and Torrenting in Canada
The question remains: Is torrenting legal or illegal in Canada?
Since January 2014, the Copyright Modernization Act of Canadian law has required local ISPs (Internet Service Providers) monitoring the BitTorrent network, like Bell, Rogers, and Telus, to take action. They started reducing internet speeds when torrenting and notifying users if they were ever caught violating copyright laws.
You won’t face fines or jail time just from a notice, but that doesn’t mean you’re safe to torrent anything. Copyright owners can still sue you in civil court if they have proof you downloaded files illegally. As a matter of fact, if the copyrighted material is being used for personal, non-commercial use, holders can sue for a maximum of CA$5,000. There just won’t be any criminal charges.
Note: These providers have the legal right to retain downloaded and uploaded data from violating users for at least six months.
Enjoy All the Benefits of Torrenting in Canada
Despite the negative connotations that come with torrenting, there’s plenty of good to it, such as:
1. Cost-effective
One big perk of torrenting is that it’s easy on your wallet. Why? Because you don’t have to shell out cash for pricey cloud storage or premium file-sharing services. Torrenting lets you transfer and access content without those extra costs, making it a popular choice for peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing.
2. Fast download speeds
Another significant advantage of torrents is the ability to download files swiftly and efficiently. The speed largely depends on the number of peers sharing the file—the more peers, the faster the downloads are.
3. Handling large files
One can easily use torrenting, and therefore P2P networks, to download or share large files. In other words, it simplifies the transfer process, which is especially beneficial when moving substantial amounts of data without the typical hassle of different methods.
4. Decentralized system
The catch with torrenting is that you can pull files from multiple sources, unlike traditional downloads from a central server. This way, if one source goes offline or the download is incomplete, other peers can fill in the gaps, and you can still finish downloading the file.
5. Interrupted downloads recovery
If you’re dealing with an unstable internet connection and your download gets interrupted, you can easily pick up on torrenting where you left off without losing progress.
Tips on How to Torrent Safely
Subscribe to a VPN
Unfortunately, what’s good and what’s not is not always clear-cut—it can sometimes be challenging to identify whether or not a file is copyrighted. It’s not the first time we’ve heard of cases where users inadvertently break the law.
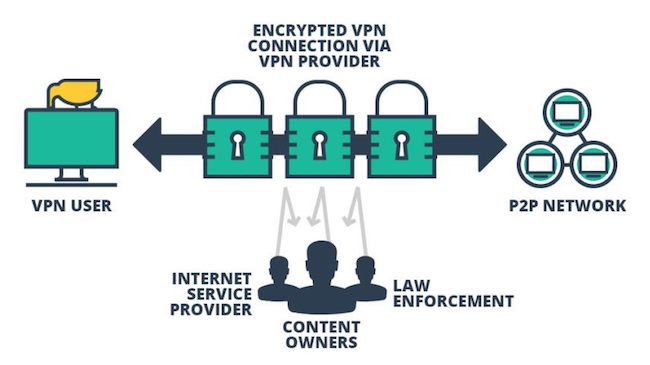
Therefore, to be sure you’re torrenting safely, we recommend using one of the best VPN providers in Canada.
A VPN, or virtual private network in short, legally allows you to safely hide your IP address and online activities from your ISP. Ensure the provider has a strict no-log policy, a robust, reliable kill switch in case your VPN connection unexpectedly drops, and extensive coverage of P2P-friendly server locations that are preferably optimized for torrenting.
We get how tempting a free VPN is. However, since these tend to be slower and have caps on bandwidth, we highly recommend opting for premium services if you plan to use them for torrenting.
Sign Up to Usenet
By signing up to a Usenet service provider—Newshosting, Eweka, Giganews, UsenetServer, TweakNews, Easynews, etc.—you’d be downloading your files from central servers rather than from a network of peers.
Speed’s generally great, and this option might even be better for privacy when torrenting since you won’t be seeding files, which means you’ll steer clear of sharing copyrighted content..
Broaden your knowledge about online privacy in our extensive guide.
Public and Private Trackers
Trackers help you find and download files on the BitTorrent network. There are two types: public and private.
- Public trackers like KickassTorrents, 1337x, RARBG and EZTV are open to everyone without needing an account. Since anyone can upload files, you have to be extra careful about what you download. So, always check the comments and the uploader’s reputation, and use antivirus software, too!
- Private trackers are more exclusive and usually require an invitation to join. Since they’re often better moderated, you get faster downloads and cleaner files without compromising safety.
Streaming vs. Downloading via Torrent: Which to Choose?
Despite all that we’ve said about torrenting so far, you can’t completely shake away the risk of getting caught. This is why many prefer to stay away and instead opt to stream the content.
The thing with streaming is that there is a lower chance of encountering illegal material. Also, laws in case you end up in the wrong alley aren’t as harsh. Some might also argue that it’s harder for copyright enforcers to track you because they can’t see who you’re sharing files with.
Still, whatever you decide to opt for, don’t ever let your guard down. I personally recommend using a VPN like Surfshark or NordVPN. This way, even if the streaming site logs your IP address, you can keep your browsing private and avoid unwanted attention altogether.
FAQ
Q: Could I end up in jail for torrenting?
A: Honestly, jail time is pretty rare for torrenting copyrighted stuff. In the worst-case scenario, you might face a fine or end up in civil court. It really depends on what you’ve downloaded and where you live.
Q: Could BitTorrent itself put malware on my computer?
A: No, BitTorrent itself isn’t usually the culprit for malware. But you’ve got to watch out for the torrent client you use—that’s where bad stuff can sneak in. Stick to well-known torrent managers, steer clear of extra software offers, and only download from sources you trust.
Q: What are seeders and leechers?
A: Right, so a seeder is someone who’s sharing the file—they’re uploading it to the network. A leecher is someone who’s downloading the file. It’s kind of an unspoken rule to upload about as much as you download. Some torrent clients even slow down your download speed if they see you’re not sharing much.
Q: Why isn’t my torrent downloading?
A: Tons of reasons could be messing with your download. It could be your internet connection, a firewall acting up, or maybe the tracker’s down. Remember, ISPs sometimes throttle BitTorrent traffic, and even search engines are getting strict, downranking links to sites with pirated content.
Q: Is torrenting music risky?
A: Yep, it can be risky. Those copyright watchdogs are always on the lookout, tracking torrents and snagging IP addresses. Then, they might hit up your ISP. Using a VPN is a smart move here—it keeps your IP address hidden.
Q: Can my ISP see the torrents I download?
A; No, they can’t see exactly what you’re downloading. But, they do have a way to peek at which sites you’re hitting up, the amount of data you’re downloading, and the specific ports you’re using. A solid VPN can really save the day here. It masks your IP address and keeps your online moves just between you and your screen.
Q: What VPN should I pick for torrenting?
A: You’d want a VPN that keeps your info locked down tight. Look for strong encryption, a solid no-logs policy, and quick servers. Don’t forget about a kill switch and servers ready for P2P sharing. I’d recommend checking out NordVPN, ExpressVPN, or Surfshark—they’re solid choices.